What size wire do I need?Updated a year ago
In order to operate correctly, an amplifier needs its power and ground wiring to be large enough to accommodate its demand for electrical current. What wire gauge (thickness) to use for power cabling depends on how much current your system will try to consume, and on how long the wiring run will be.
Understanding the needs of your system can help you know when to choose 4-gauge wire instead of 8-gauge wire. Do a little bit of math and then consult our wire size chart below. Of course, if you're looking for a new car amplifier, we list the recommended amp wiring kit with each amp.
The Formulas For Calculating Current Draw:
To determine the approximate current draw (in amperes) of your amplifier, you must first calculate the total power of the system. Multiply the number of channels by the number of RMS watts per channel. If you have multiple amps, add up the total RMS power figures to arrive at a grand total.
Generally speaking, there are two kinds of amplifiers — Class D and Class AB — so there are two formulas for calculating current draw. (You can read the detailed explanation below the chart.) You use the formula that applies to your amplifier. If you don't know what Class your amplifier is, use the Class AB calculations for the safest result.
Class D amplifier: total RMS Wattage divided by 0.75 Amp Efficiency divided by 13.8 Volts equals Current Draw in Amperes
Class AB amplifier: total RMS Wattage divided by 0.50 Amp Efficiency divided by 13.8 Volts equals Current Draw in Amperes
The resulting figure is your system's approximate maximum current draw, whichever kind of amplifier you have. Compare this number to the numbers in the "Amperes" column in the chart below. Now figure out the cable length you'll need — that's the distance from your battery to the amplifier's mounting location. Cross-reference these two figures in the chart to determine which gauge of cable you need.
Please note that the smaller the gauge number, the larger the wire. 1/0 ("one-aught") is the common name for a 0-gauge wire; 2/0 ("two-aught") for a 00-gauge wire.
Wire Size Calculator
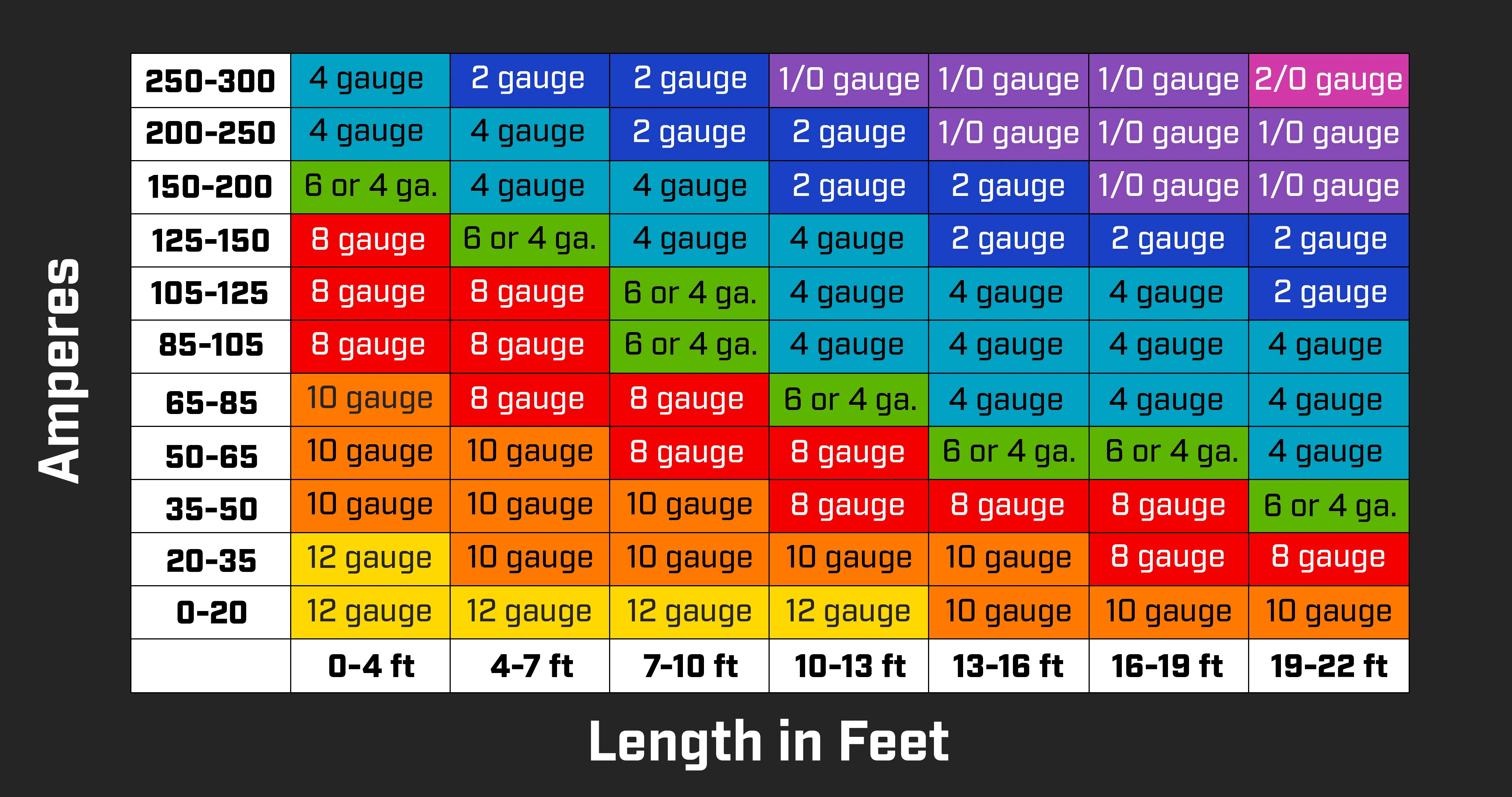
Note: This chart is for copper wire only. Copper-clad aluminum (CCA) wire cannot handle the amount of current that a copper wire of the same size can.
A more detailed explanation
Here's a breakdown of the formulas we employ for those seeking further insights. While determining the amplifier's total power is relatively straightforward, understanding other components can prove challenging.
Calculating Current: Joule's Law
Current (in Amperes) equals Power (in Watts) divided by Voltage (in Volts).
However, no amplifier is 100% efficient
The initial formula overlooks the inherent inefficiency in power production. It's essential to incorporate this factor.
Current (in Amperes) equals Power (in Watts) divided by Amplifier Efficiency (expressed as X%) divided by Voltage (in Volts).
By integrating this inefficiency for each amplifier class, we derive the two aforementioned formulas.
The formula for Class D amps
A typical Class D amplifier is about 75% efficient, which means about three quarters of the power it generates is turned into audio output while one quarter of the power is lost as heat. So if the amplifier is putting out 400 watts, it's actually drawing about 533 watts of power from its source, and the amp's wiring needs to be big enough to handle that draw.
A Class D amplifier's Current Draw equals its RMS output Wattage divided by 75% Efficiency divided by 13.8 Volts
The formula for Class AB amps
A typical Class AB amplifier is about 50% efficient, which means about half of the power it generates is turned into audio output while the other half of the power is lost as heat. So if the amplifier is putting out 400 watts, it's actually drawing about 800 watts of power from its source, and the amp's wiring needs to be big enough to handle that draw.
A Class AB amplifier's Current Draw equals its RMS output Wattage divided by 50% Efficiency divided by 13.8 Volts
Automotive voltage is neither 12 volts nor 14.4 volts
While vehicles indeed operate on a 12-volt electrical system, assuming the vehicle is running, its alternator typically boosts the system voltage to around 13.8 volts. This more accurately reflects real-world conditions. Dividing by 12 yields a larger number, potentially indicating a larger wire gauge, although it often falls within the same color range on the chart. Manufacturers may use 14.4 volts in their specifications to exaggerate power ratings.
Resistance increases with wire length
Differing cable lengths have distinct ratings because electrical resistance, inherent in all wire, accumulates as the cable lengthens. Eventually, this resistance causes the voltage to drop below a usable level. Upsizing the power cable restores the voltage to its intended level.
Wire size matters for current flow
According to our tech support team, the primary performance limitation in most amplifier installations stems from inadequate current delivery — either due to a weak ground or insufficient wire gauge. Installing too small a wire gauge leads to poor performance, potentially reduces the service life of connected components (such as amplifiers and speakers), and poses a safety hazard.
Conversely, there's no significant downside to installing a larger wire gauge, and it may even enhance performance. While purchasing excessively large gauge wiring, like 2-gauge instead of 10-gauge, would be wasteful, opting for the larger wire size when the chart allows for flexibility is the prudent choice.
What size speaker wire do I need?
Speaker wiring matters too. The signal and power coming out of your amplifier must not be impeded on their way to your speakers and subs. When you replace or run new speaker wiring, we recommend using:
- 18-, 16-, or 14-gauge wires for speakers
- 16-, 14-, or 12-gauge wires for subwoofers
As with the power wire, the longer the run and the more current you're pushing through it, the larger size you should use. For example, if your amp is in the trunk and you're sending 100 watts to your front speakers, 14-gauge speaker wire is a good call. But if the amp is only 50 watts, 16-gauge would be fine.